
Project Description
As part of the project, students study the average speed of their commute to school. Before starting the investigation, they formulate two clear hypotheses that can be tested using data analysis. For example, they may assume that commute time differs depending on the day of the week or time of day. After completing the study, students draw conclusions based on the obtained results and analyze how accurate their hypotheses were. The main analytical tool in this project is descriptive statistics. Students calculate indicators such as the median, quartiles, mean, and standard deviation. They also visualize the data using a boxplot, which helps identify variability and potential outliers.
Gallery
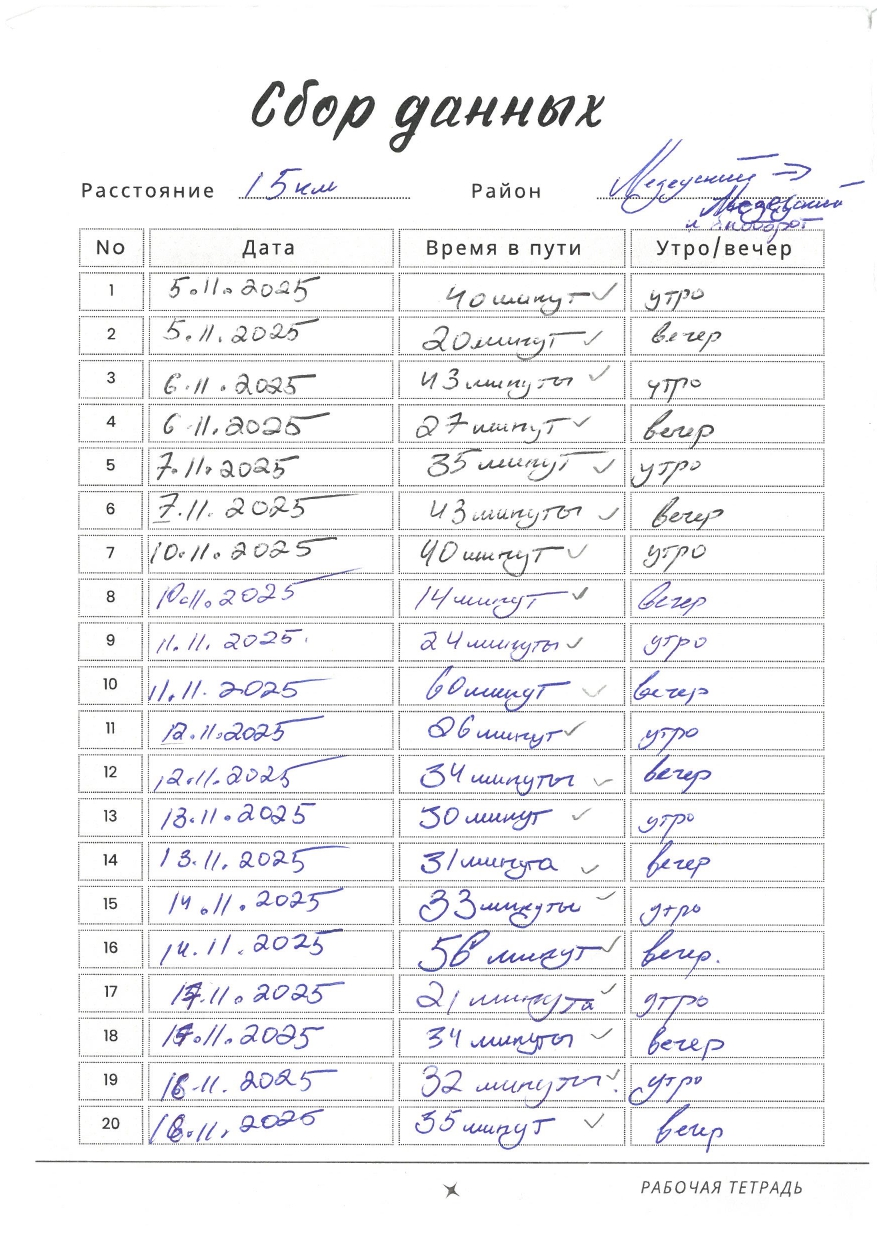
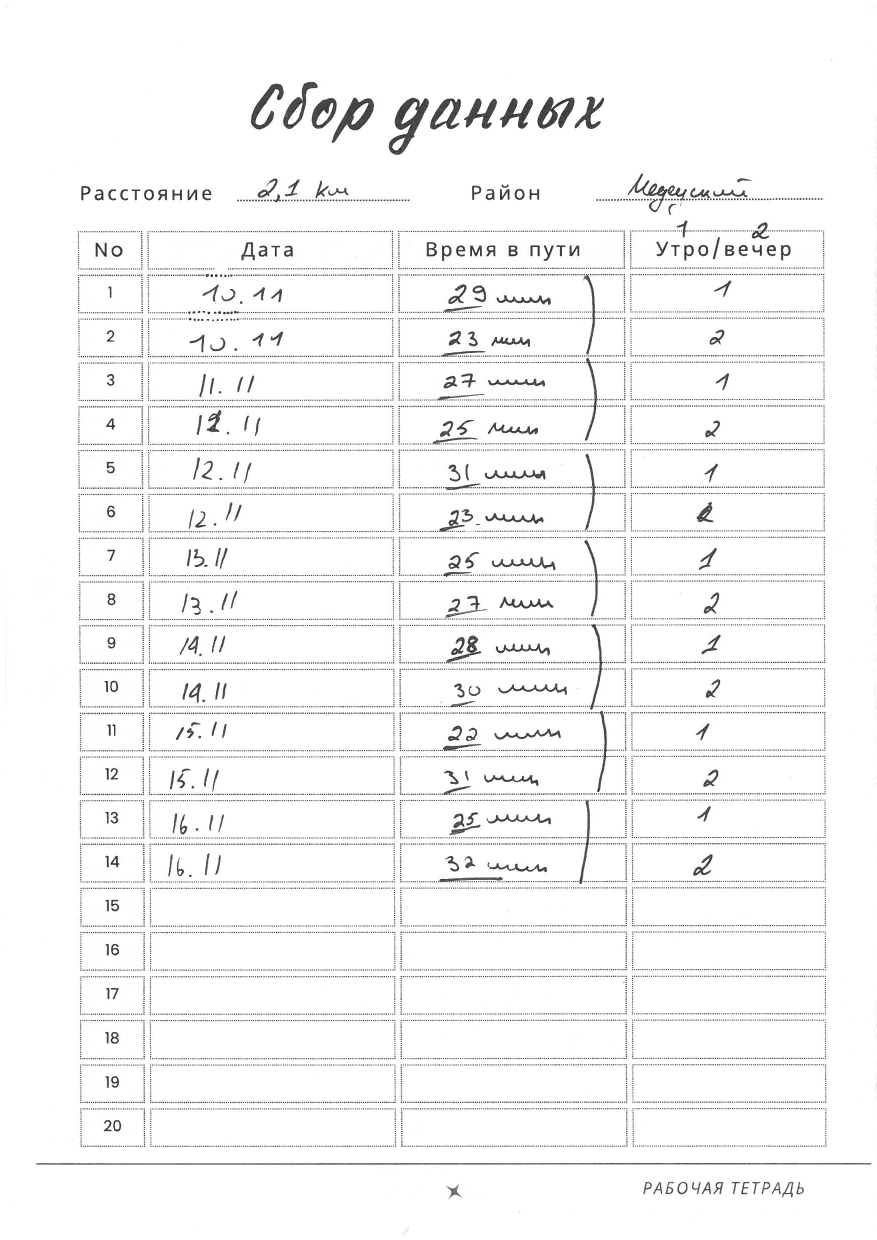
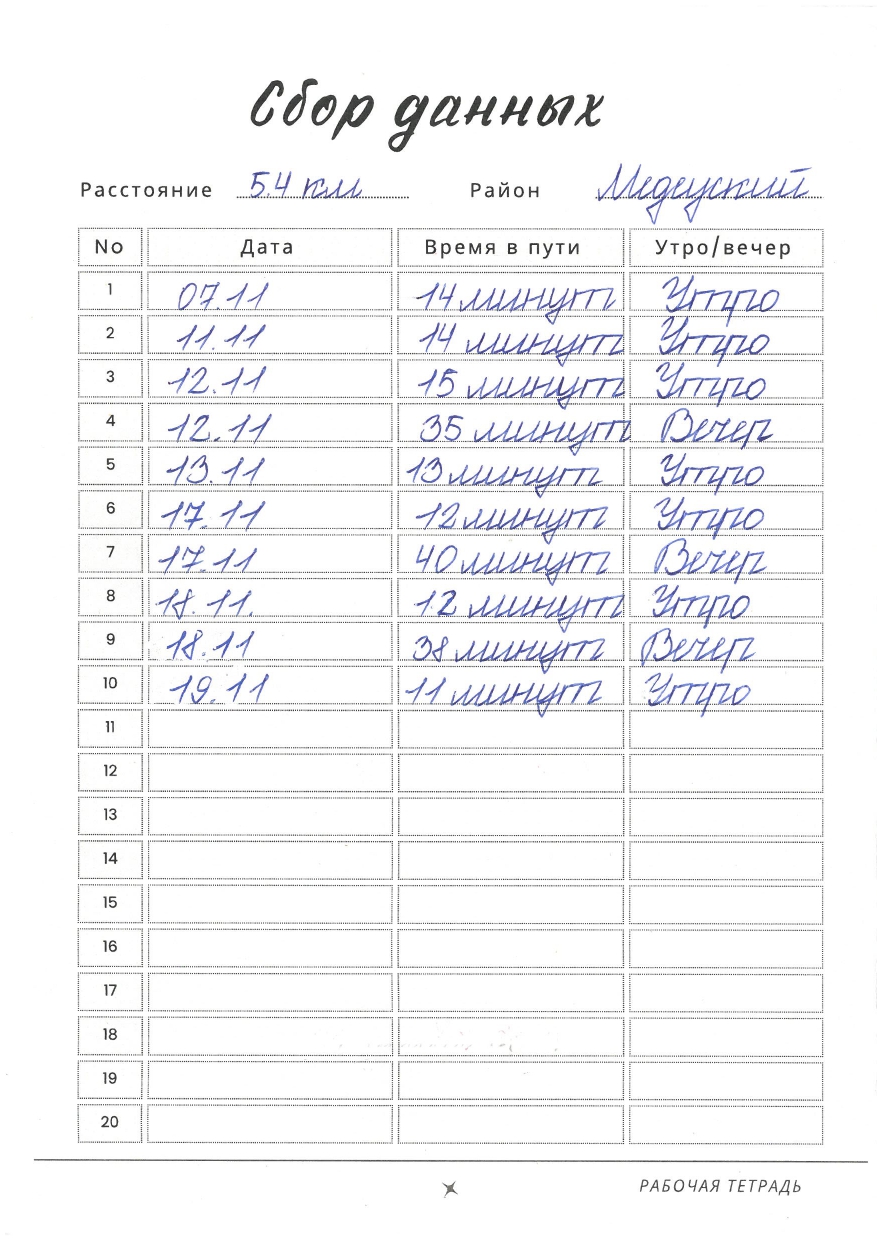
Stage 1: Data Collection
At the first stage, students collect commute-time data over one or two weeks and record their measurements in their notebooks. Ideally, the total sample size across the class should be at least several hundred observations. After data collection, all entries must be transferred into an Excel table and submitted to the teacher for verification.
Gallery



Stage 2: Data Analysis
At this stage, students analyze the collected data by calculating key descriptive statistics: quartiles, median, mean, and standard deviation. Each student should ideally have around 15–20 observations. Then they create a boxplot to visualize the distribution. The teacher collects all individual Excel files, merges them into a combined dataset, and builds a class-wide boxplot to compare results and discuss findings.
Gallery



Stage 3: Conclusions
At this stage, students formulate conclusions based on the analyzed data and check their initial hypotheses. They discuss identified patterns and trends, determine whether their assumptions were confirmed, and analyze possible sources of error or variability. The teacher conducts a whole-class discussion, summarizes results, and encourages students to reflect on how their findings relate to real-life situations.